Why does every skin specialist recommend sunscreen? What the sun does to our skin...
What Does the Sun Do to Our Skin?
The sun has a significant impact on our skin, both beneficial and harmful. While sunlight is essential for processes like vitamin D synthesis, excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can lead to various skin issues.
Here’s a detailed look at the effects of the sun on our skin:
Positive Effects of Sun Exposure
1. Vitamin D Production:
- Synthesis: Sunlight is essential for the synthesis of vitamin D in our skin. UVB rays convert cholesterol in the skin into vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.
- Mood Improvement: Sun exposure can boost the production of serotonin, a hormone associated with mood elevation, helping to combat conditions like seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Negative Effects of Sun Exposure
1. Sunburn:
- Acute Damage: Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive UVB radiation, causing redness, pain, and swelling. Severe sunburns can result in blistering and peeling.
- Cell Damage: UV radiation damages skin cells, leading to DNA mutations that can increase the risk of skin cancer.
2. Premature Aging (Photoaging):
- Wrinkles and Fine Lines: UV radiation, particularly UVA rays, breaks down collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging.
- Loss of Elasticity: The skin becomes less firm and more prone to sagging as collagen production decreases.
- Hyperpigmentation: Sun exposure can cause uneven skin tone, dark spots, and pigmentation disorders like melasma.
3. Skin Cancer:
- Types of Skin Cancer: Prolonged and unprotected sun exposure increases the risk of various types of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
- DNA Damage: UV radiation causes direct DNA damage in skin cells, leading to mutations that can trigger cancerous growth.
How the Sun Affects Collagen
Collagen is a crucial protein in the skin that provides structure, elasticity, and firmness.
While sunlight is essential for producing vitamin D, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can have detrimental effects on collagen.
This leads to premature skin aging and other skin issues. Here's a closer look at how the sun affects collagen:
The Role of Collagen in the Skin
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the skin, making up about 75-80% of its dry weight.
It forms a fibrous network in the dermis (the middle layer of the skin) that supports the skin’s structure and elasticity.
As we age, collagen production naturally decreases, leading to the formation of wrinkles and sagging skin. External factors, such as sun exposure, can accelerate this process.
UV Radiation and Collagen
Sunlight consists of different types of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, primarily UVA and UVB rays. Both types of UV rays can damage the skin, but they do so in different ways:
1. UVA Rays:
- Penetration: UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, reaching the dermis where collagen resides.
- Damage: These rays generate free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause oxidative stress. This oxidative stress damages collagen fibers and impairs the skin’s ability to produce new collagen. Over time, this leads to the breakdown of existing collagen, resulting in wrinkles, loss of skin elasticity, and sagging.
2. UVB Rays:
- Penetration: UVB rays primarily affect the outer layer of the skin, the epidermis.
- Damage: UVB rays are responsible for causing sunburn. Although they do not penetrate as deeply as UVA rays, they can still contribute to collagen damage by triggering inflammation and cellular damage in the skin’s upper layers. This can indirectly affect the deeper layers by disrupting the overall skin structure and health.
Photoaging
The term "photoaging" refers to the premature aging of the skin caused by repeated exposure to UV radiation. Photoaging is characterized by:
- Wrinkles and Fine Lines: Due to the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers.
- Hyperpigmentation: UV exposure can lead to uneven skin tone, dark spots, and freckles.
- Dryness and Rough Texture: Sun-damaged skin often becomes dry and rough due to the degradation of collagen and other structural proteins.
- Loss of Elasticity: The skin becomes less firm and more prone to sagging as collagen levels decrease.
Protection and Prevention
To protect your skin's collagen from the harmful effects of UV radiation, consider the following measures:
1. Sunscreen:
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays. Apply sunscreen generously and reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
2. Protective Clothing:
- Wear protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses to shield your skin from direct sun exposure.
3. Seek Shade:
- Avoid direct sunlight during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) when UV radiation is strongest.
4. Antioxidants:
- Incorporate antioxidants into your skincare routine and diet. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, protecting collagen from damage.
5. Avoid Tanning Beds:
- Tanning beds emit UV radiation that can be even more intense than natural sunlight, significantly increasing the risk of collagen damage and skin cancer.
Conclusion
While sunlight is beneficial for overall health in moderation, prolonged and unprotected exposure to UV radiation can significantly damage collagen, leading to premature skin aging and other skin issues.
By taking preventive measures such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and incorporating antioxidants into your skincare routine, you can help protect your skin’s collagen and maintain a youthful, healthy complexion.
OK, so none of us a perfect...... There are ways to promote collagen:
How to Produce More Collagen in Your Skin
Collagen is a vital protein that provides structure, elasticity, and strength to your skin. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and a loss of firmness.
However, there are several ways to stimulate collagen production and maintain youthful, healthy skin. Here’s how you can boost collagen levels:
1. Topical Treatments
Retinoids (Vitamin A Derivatives):
- Function: Retinoids are known for their ability to increase collagen production by promoting cell turnover and stimulating fibroblasts.
- Usage: Over-the-counter options like retinol or prescription-strength retinoids such as tretinoin can be incorporated into your skincare routine.
Vitamin C:
- Function: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps protect against UV damage and supports collagen synthesis by stabilizing collagen fibers.
- Usage: Apply a topical vitamin C serum in the morning to boost collagen production and brighten the skin.
Peptides:
- Function: Peptides are short chains of amino acids that can penetrate the skin and signal cells to produce more collagen.
- Usage: Look for skincare products containing peptides and incorporate them into your daily regimen.
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs):
- Function: AHAs, such as glycolic acid, exfoliate the skin, promoting cell turnover and stimulating collagen production.
- Usage: Use AHA-based exfoliants or serums regularly to enhance skin texture and firmness.
2. Healthy Diet
Protein-Rich Foods:
- Sources: Include lean meats, fish, eggs, beans, and legumes in your diet to provide the building blocks for collagen synthesis.
Vitamin C-Rich Foods:
- Sources: Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli are rich in vitamin C, which is essential for collagen production.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods:
- Sources: Berries, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds contain antioxidants that protect collagen from free radical damage.
Collagen Supplements:
- Types: Hydrolyzed collagen peptides are easily absorbed by the body and can help support skin elasticity and hydration.
- Usage: Incorporate collagen supplements into your diet as directed to boost overall collagen levels.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Sources: Foods like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts contain omega-3 fatty acids that help maintain healthy skin and reduce inflammation.
3. Professional Treatments
Micro-Needling:
- Process: Micro-needling involves creating tiny punctures in the skin to stimulate the body's natural wound-healing process, which boosts collagen production.
- Benefits: This treatment improves skin texture, reduces wrinkles, and enhances overall firmness.
Laser / IPL Therapy:
- Types: Fractional lasers and non-ablative lasers stimulate collagen production by heating the deeper layers of the skin.
- Results: Laser treatments can help improve skin tone, texture, and elasticity.
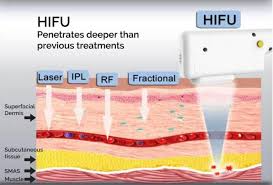
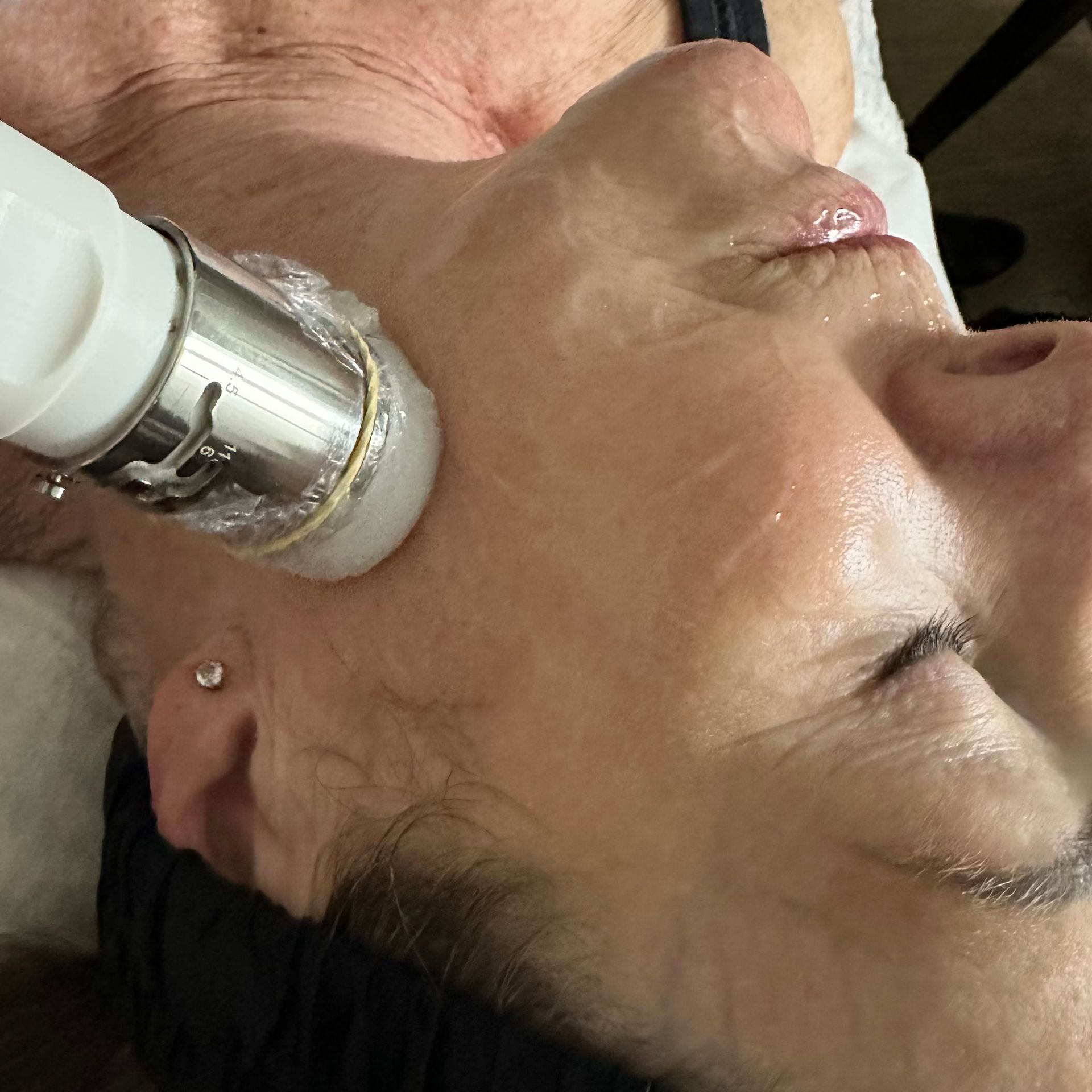
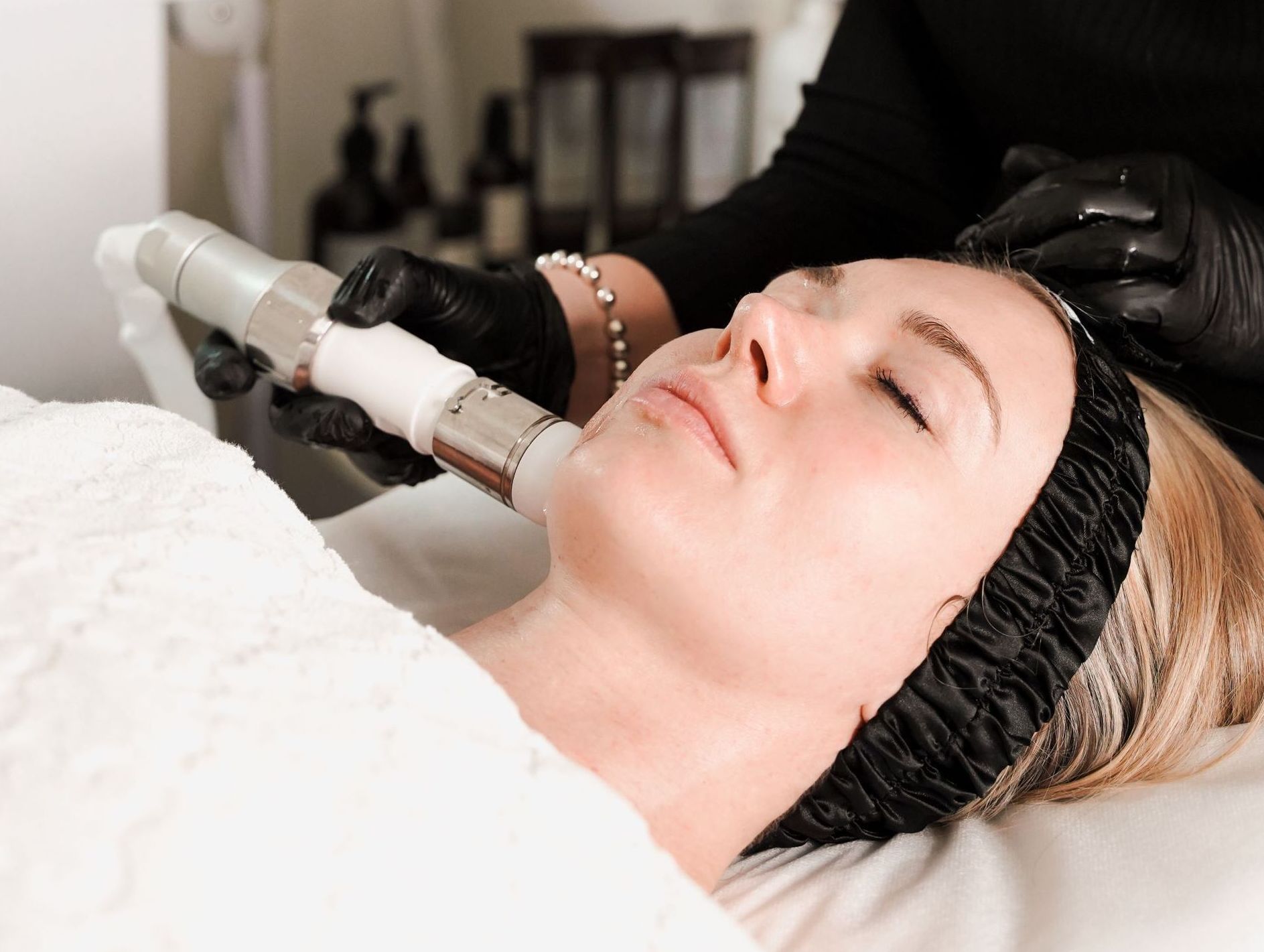
HIFU treatments
- Mechanism: HIFU treatments use ultrasound energy to heat the dermis the epidermis and the SMAS layer, stimulating collagen production in all 3 layers without damaging the surface of the skin.
- Advantages: These treatments can tighten skin, reduce wrinkles, and improve skin firmness.
Chemical Peels:
- Action: Chemical peels remove the outer layer of dead skin cells, promoting cell turnover and collagen synthesis.
- Outcome: Regular chemical peels can enhance skin texture, reduce fine lines, and boost collagen levels.
Conclusion
Boosting collagen production in the skin involves a combination of topical treatments, a healthy diet, lifestyle changes, and professional treatments.
By incorporating retinoids, vitamin C, peptides, and AHAs into your skincare routine, eating a balanced diet rich in protein, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids, protecting your skin from UV damage, and considering professional treatments like micro-needling, HIFU and laser therapy, you can maintain youthful, firm, and healthy skin.